Email: info@karssenmetal.com Tel: +86 18147353336
Graphitization is a process of graphitization of carbon materials at high temperatures above 2000 degrees Celsius. There are few materials in nature that can adapt to high temperatures of 2000-3000 degrees Celsius. Only carbon materials are materials that can withstand high temperature, corrosion, and conduct electricity. Therefore, the carbon material is also the main structural material of the graphitization furnace.
Acheson Graphitization Furnace
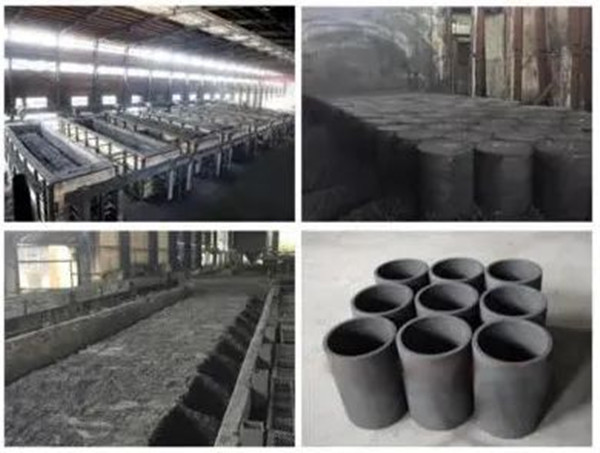
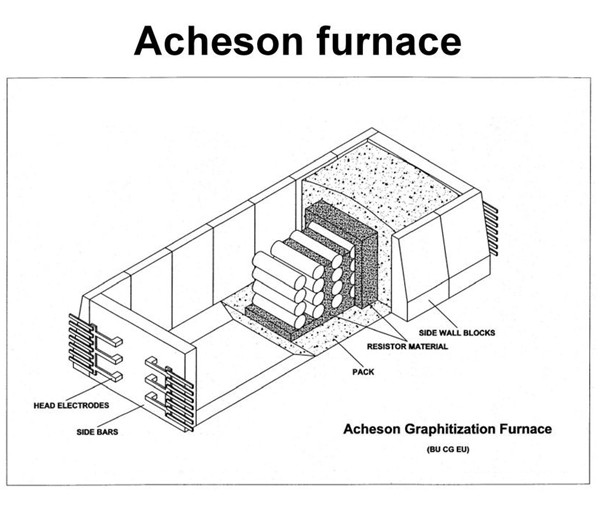

Since Acheson obtained a patent for the production of graphite products in the United States in 1895, the Acheson-type graphitization furnace based on Acheson's principles has been continuously improved. However, furnace materials, furnace structure, furnace technology, and furnace energy consumption have not progressed much. It was not until the 1960s that the AC furnace was improved to a DC furnace that the graphitization technology changed. Both the DC graphitization furnace and the AC graphitization furnace belong to the Acheson furnace. Compared with the AC graphitization furnace, DC graphitization technology has begun to develop in developed countries in Europe and America. Compared with the AC graphitization furnace, it has significant advantages such as large capacity, good product quality and low energy consumption, which has attracted widespread interest and attention from all over the world.
Kastner Furnace (Lengthwise Graphitization Furnace)
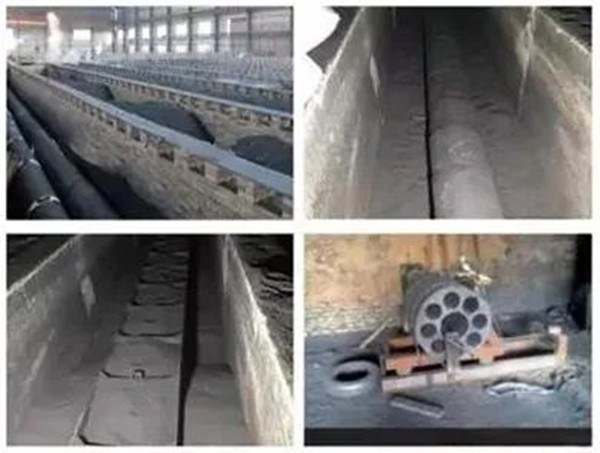
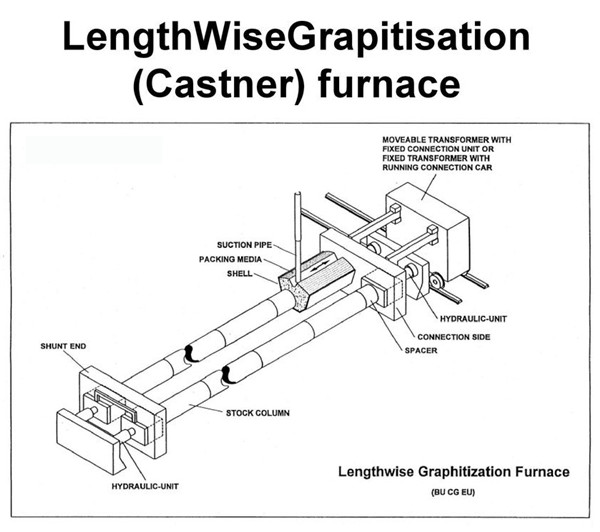

It is a kind of resistance furnace that directly connects the electric current into the baked products in series, uses the resistance of the product itself to convert the electric energy into heat energy, and graphitizes the products. It was first invented and patented by Castner in 1896. It is characterized by energy saving and fast graphitization.
The above two graphitization processes are intermittent, with high energy consumption, large pollution and difficult purification.
Carbon-savvy people are working hard to find a better graphitization method, hoping that the continuous graphitization process will become the mainstream process.
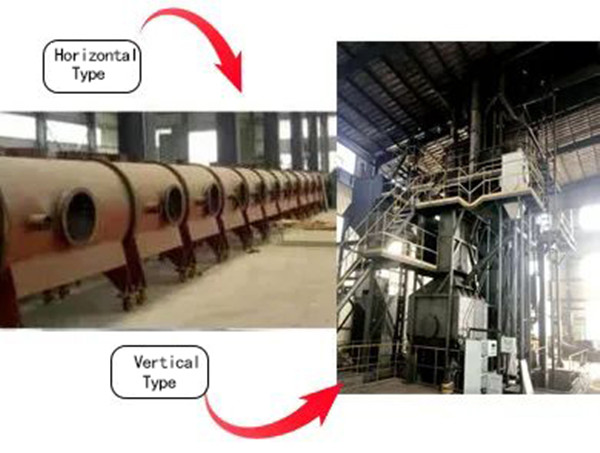
Continuous graphitization furnace
When the graphitization temperature reaches 3000K, the theoretical power consumption of graphitization for 1 ton of baked products is 1360kwh. The actual power consumption of graphitization in the production of carbon products is usually 4000-5500kwh/t, which is 3~4 times of the theoretical power consumption. Therefore, reducing the power consumption of graphitization in carbon production has always been a research topic that engineers and technicians attach great importance to, and it is also the key to reducing costs and improving benefits for carbon product manufacturers.
Graphitization furnace is one of the key equipments for the production of carbon products and also one of the equipments with the largest energy consumption.
The production of carbon-graphite products requires a large amount of energy and energy consumption, which accounts for about 30% to 40% of the production cost of carbon products. The graphitization process in the carbon production process is also a major energy consumer, and its power consumption accounts for about 70% of the total power consumption of product production.
Therefore, the research and improvement of the graphitization process and the graphitization furnace, as well as the improvement of the quality of the graphitized products, have always been the important missions of carbon engineering and technical personnel.
Isostatic graphite blocks are an important graph
Graphite rotor belongs to graphite material, whi
Graphite sheets have many important roles in the
Contact: Bateer
Phone: +86 18147353336
Tel: +86 18147353336
Email: info@karssenmetal.com
Add: Room D204-2203, Innovation Building, Baotou Light Industry Vocational Technical College, 19 Jianhua Road, Qingshan District, Baotou City, Inner Mongolia, China.